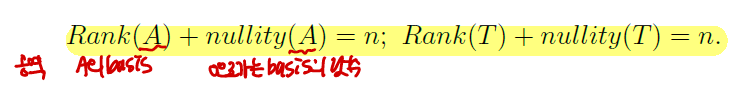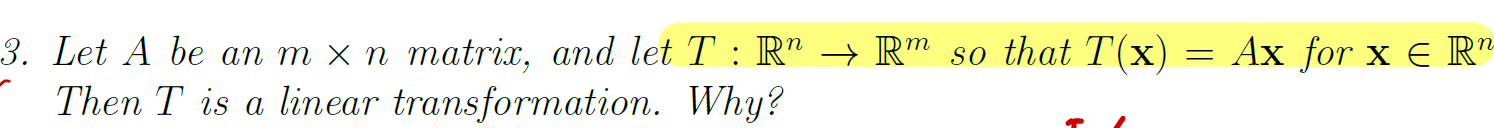4.1 projections the Gram-Schmidt orthogonalization procedure to obtain an orthogonal basis v, w ∈ Rn. Then the vector p in sp({w}) that is closest to v,, sp({w}) 에 포함된 벡터 p는 v와 제일 가깝다. vector p : the projection of v onto the subspace sp({w}) v = p + v − p and v − p ∈ sp({w})⊥ the decomposition v = p + v − p is unique the concept of projection onto a linear span of a vector to the general subspac..